The Pillars of Ashoka are one of India’s most impressive historical landmarks, built by Emperor Ashoka of the Maurya Dynasty in the 3rd century BCE. These pillars mark his journey from a fierce warrior to a peaceful ruler, inspired by the teachings of Buddhism. Known for their towering presence and powerful inscriptions, the Pillars of Ashoka are spread across various locations in India, each carrying messages of kindness, morality, and respect for life. They reflect Ashoka’s deep belief in dharma and his desire to encourage peace throughout his empire. Each ashok pillar holds an incredible story and stands as a testament to the emperor’s ideals.The Story Behind the Pillars of Ashoka
The History of Ashoka’s pillars dates back to a transformative time in Emperor Ashoka’s life. After witnessing the immense bloodshed of the Kalinga War, Ashoka was filled with remorse. This moment changed him, leading him to embrace Buddhism and its message of compassion. To spread these ideals, Ashoka had the Pillars of Ashoka constructed across his empire, each engraved with messages promoting kindness, non-violence, and the value of moral life.
Ashoka’s change was profound, and he wanted his subjects to follow a similar path of peace and ethical living. So, he had these Ashoka Pillars in India placed in key locations, such as religious sites and trade routes, to reach as many people as possible. The Pillars of Ashoka history isn’t just about the emperor’s transformation, it’s also about using these pillars as a way to shape society toward a gentler way of life.
Suggested Read: Pushkar Mela Rajasthan 2024
Design and Symbols on the Pillars
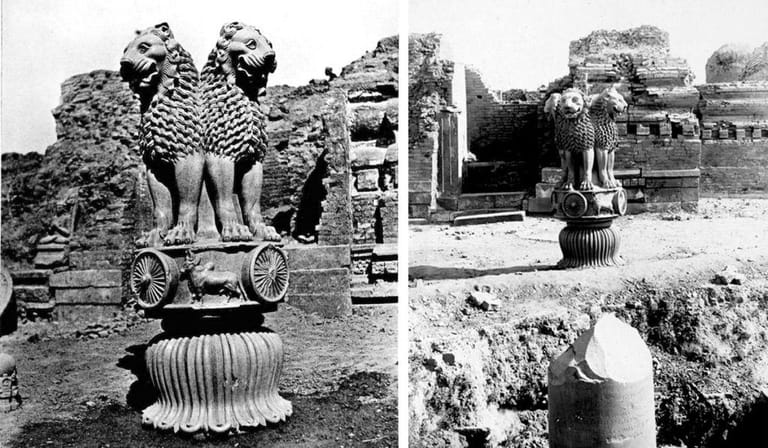
The Pillars of Ashoka were crafted from sandstone, standing between 40 and 50 feet high, showcasing the skill of ancient Indian artisans. The most famous Original Ashoka Pillar is the Lion Capital of Ashoka at Sarnath, which is now India’s national emblem. It features four lions standing back-to-back, symbolizing strength, courage, and unity. Many pillars also display other animals, each with a symbolic meaning.The inscriptions on these Pillars of Ashoka were written in Brahmi script, which was commonly understood by people at that time. This meant Ashoka’s messages on compassion and morality were accessible to his subjects. The Ashok Chakra and Ashok Stambh at the top of some pillars symbolize the cycle of life, and the wheel is now on the Indian flag as a symbol of India’s moral values and unity. The Pillars of Ashoka aren’t just historical artifacts, they’re works of art that reflect the empire’s commitment to a higher set of moral values.
Suggested Read: Coldest Places in India
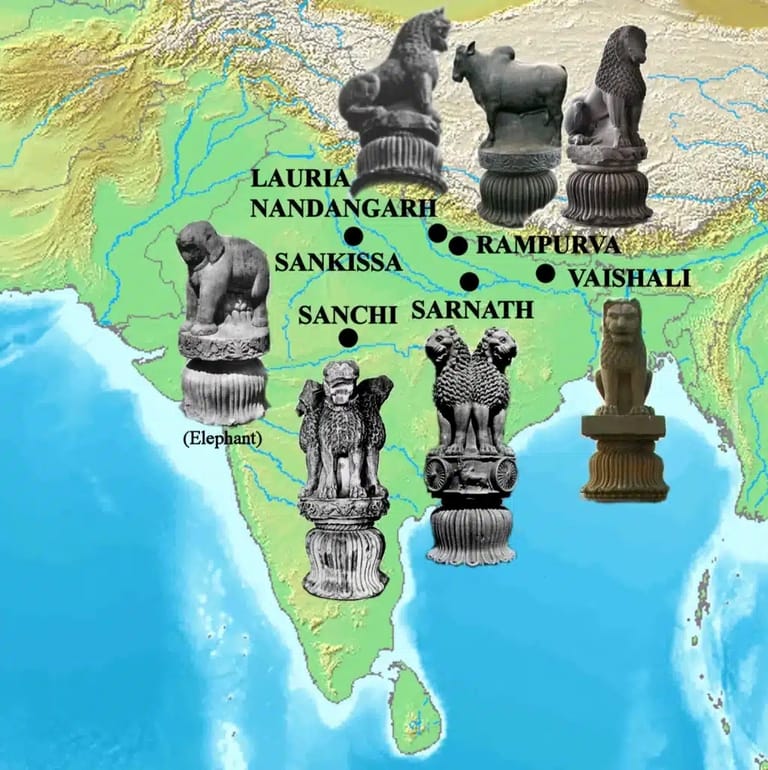
Key Locations of Ashoka Pillars in India
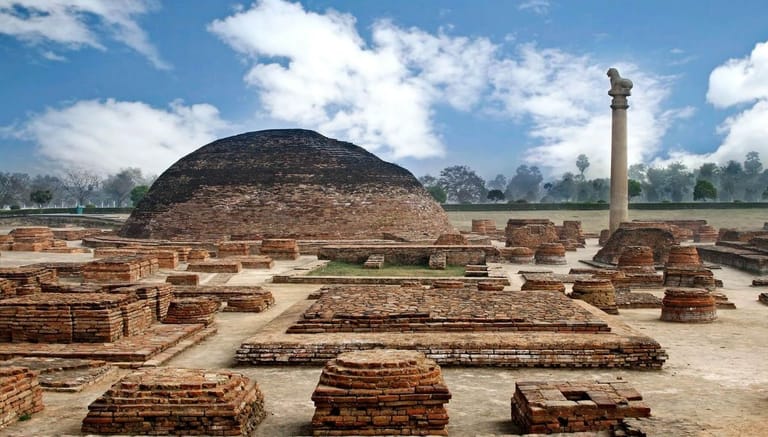
The Ashoka pillar locations are spread across India, with some pillars even found outside the country. Notable Ashoka Pillars in India include those at Sarnath, Vaishali, Sanchi, and Delhi. The Sarnath pillar is especially significant, marking the spot where the Buddha delivered his first sermon. Other pillars are scattered in places like Allahabad, Lauriya Nandangarh, and Rampurva, each bearing unique messages and artwork that represent different aspects of Ashoka’s teachings.These Pillars of Ashoka have become major attractions, drawing tourists, historians, and researchers who wish to understand Ashoka’s philosophy. Many people visit these Ashoka Pillar locations to learn about the emperor’s transformation and the impact he aimed to make on society.
Suggested Read: International Airports in India
Importance and Legacy of the Ashoka Pillars
The Importance of Ashoka Pillars is significant in Indian history and culture. These Pillars of Ashoka are reminders of a ruler who transformed from a conqueror into a champion of peace. They show how he prioritized the well-being of his people and the promotion of dharma. Through the pillars, he encouraged non-violence, kindness to animals, and respect for all forms of life.The Pillars of Ashoka facts are fascinating to historians because they provide insights into ancient Indian society, governance, and Ashoka’s personal beliefs. One intriguing fact is that despite their age, many Pillars of Ashoka are still standing, which speaks volumes about the high quality of craftsmanship during Ashoka’s reign. The Ashok ka stambh, as these pillars are known in Hindi, remains a revered cultural symbol in India.
The Lasting Impact of Ashoka’s Pillars
Today, the Pillars of Ashoka stand as important heritage sites. The Ashoka Pillars in India continue to inspire with their messages, and many are protected as historical monuments. They symbolize India’s long-standing values of peace, respect, and unity, which are still celebrated today. Replicas of the Ashok pillar can be seen in various public spaces, and the Lion Capital of Ashoka is present on India’s official documents and currency.The Pillars of Ashoka are not just stone structures, they carry the essence of a ruler who chose peace over power and sought to build a society based on moral values. These Pillars of Ashoka are symbols of India’s cultural depth and remain relevant as reminders of the strength found in compassion and ethical governance.